The Motherhood Penalty: Overcome this Career Advancement and Wage Blocker
Guest contributed by Josie Sutcliffe

Image via Shutterstock
Despite considerable attention, the gender wage gap has only improved by 8% in the last 20 years — a slow pace of improvement that indicates removing the gap entirely is more than a generation away.
What’s holding up progress?
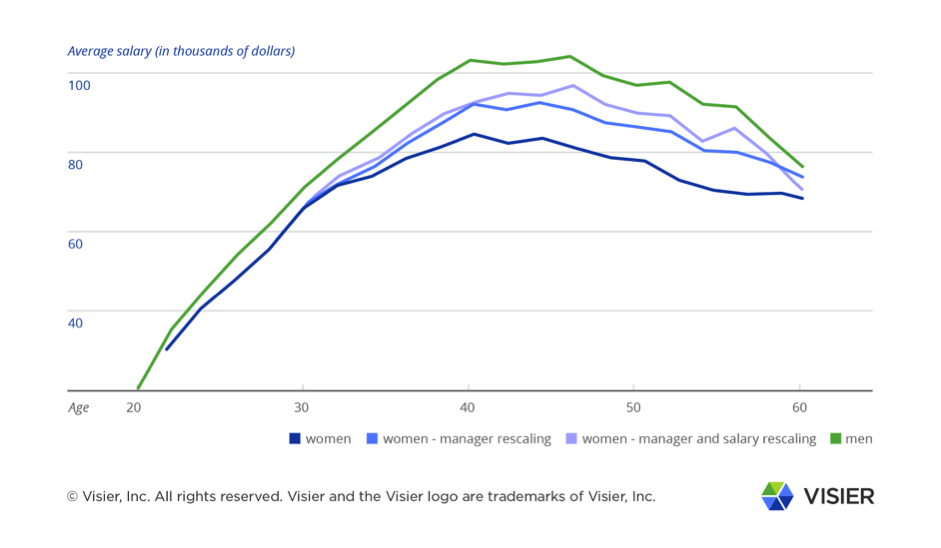
A Visier Insights report analyzed an aggregated database of over 160,000 US-based employees of over 30 large US enterprises and found that there’s an underrepresentation of women in manager positions — in particular during the key childcare years — directly driving the overall gender wage gap. This finding is known as the Manager Divide and has a strong correlation to motherhood.
The Motherhood Penalty
Simply put, during the key childcare years women are increasingly less likely to hold manager positions, which directly impacts their average earnings compared to men.
At the time the gender wage gap begins to widen (starting with women at age 32 earning on average 90% the wages of men and decreasing to just 82% by age 40), women are increasingly underrepresented in manager positions. This directly drives the gender wage gap as managers earn on average two times the salary of non-managers.
The Manager Divide occurs during the key childcare years: most women in the US who have children give birth to them between the ages of 25 and 34. And with most children entering school (and, therefore, requiring less childcare) at age 5, women who have children are most likely to experience increased childcare demands up until the age of 39. Despite an increased trend towards equal parenting, in today’s society women still typically take on more of the family care responsibilities. These responsibilities impact their careers.
It’s worth noting that, when reviewing promotion events by age, there is no significant difference in the overall rate of promotions in any age range for women or men. In other words, women are promoted at the same rate as men during the Motherhood years, but men are more likely to be promoted into manager.
If the Manager Divide was removed and, therefore, the same proportion of women held manager positions as men, the gender wage gap across all workers would be reduced by just over one third for those over age 32. If this “augmented” population of female managers were then given the same average salary as male managers, the gap would be cut in half.
Taking Steps to Finally Close the Gender Wage Gap
If a company pays women and men the same for equal work, but then underrepresents women in the better-compensated manager roles, that company has not achieved gender equity.
Here are some actions leaders can take to promote and ensure gender equity:
- Get a high-level understanding of the state of gender equity within your organization. Start with simple metrics like “female ratio” (looking at the percent of total headcount that are female) by department, role, and/or location, and in your hiring pipelines.
- Dig deeper by finding out if pay and performance ratings are unbiased for men and women. Compa-ratio is a classic compensation calculation that indicates how close a person’s base pay is the pay level midpoint for the role they perform. If women have a lower than average compa-ratio, then it is likely that pay decisions are not being made equitably. Similarly, understanding the proportion of employees who receive each level of performance rating and then comparing this to the proportion of each rating for female employees will uncover if performance ratings are handed out in an unbiased manner.
- Measure not only promotions by gender, but also the nature of the promotions: by role, department, or location, find out if the percent of women promoted to or holding manager positions is lower than the percent of men promoted to or holding manager positions.
- Take steps to correct gender inequity, starting with your processes for hiring and promotion. Implement the Rooney Rule: for every manager position you have open to fill, consider “at least one woman and one underrepresented minority” in your slate of candidates. Consider blind screening of resumes (removing names or other gender identifiers from resumes) when selecting applicants for interviews. And introduce consistent and gender bias-free performance management processes.
- Given that the Manager Divide is connected to the years when women are most likely to have increased childcare demands, look into ways your organization can better support paid parental leave. It should be equally available to mothers and fathers, and be socially acceptable not just for mothers, but also for fathers to take. Flexible working time arrangements could be a key part of your solution.
Make the business case for gender equity at your organization. It isn’t just about fairness, avoiding lawsuits, and protecting (or building) your employer brand (check out the InHerSight for an idea of what the future holds — a Glassdoor-type site that focuses on rating companies from the perspective of their support of women). Research by McKinsey shows that companies in the top quartile for gender diversity are 15% more likely to have financial returns above their respective national industry medians. According to a 2016 McKinsey Global Institute report, if full gender equality is attained, $4.3 trillion could also be added to the U.S. economy by 2025.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions of Guest contributors are not necessarily those of theglasshammer.com